The adhesion of adhesive is a cornerstone of countless industries, enabling materials to bond effectively for everything from consumer products to aerospace components. But what drives this phenomenon? How do adhesives achieve such remarkable feats of bonding, and what innovations are shaping their future? This article delves into the science behind adhesive adhesion, explores its applications, and highlights advancements that are redefining its capabilities.
What Is Adhesion of Adhesive?
Adhesion refers to the process by which an adhesive binds two surfaces together. Unlike cohesion, which involves forces within the adhesive material, adhesion relies on interactions between the adhesive and the substrate surfaces.
Key Components of Adhesion
- Surface Energy: Affects how well the adhesive wets the substrate.
- Chemical Bonds: Include covalent, ionic, or hydrogen bonding.
- Mechanical Interlocking: Physical grip achieved through surface roughness.
Types of Adhesive Bonding
- Structural Adhesives: Provide strength and durability.
- Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives: Used in tapes and labels.
- Reactive Adhesives: Cure chemically to form bonds.
How Adhesion Works: The Science Behind It
Adhesion occurs due to the interplay of various forces and principles. Understanding these factors reveals why some adhesives excel in specific applications.
Surface Wetting and Bond Formation
- Adhesion begins with the adhesive spreading across the surface, a process influenced by the substrate’s surface energy.
- The adhesive must displace air and contaminants to form a robust bond.
Intermolecular Forces at Play
- Van der Waals Forces: Weak attractions contributing to adhesion.
- Hydrogen Bonds: Stronger forces that enhance adhesive strength.
- Electrostatic Interactions: Occur in specific adhesive systems.
Factors Influencing Adhesion Strength
Surface Preparation
Clean, dry, and rough surfaces promote better bonding. Contaminants, such as oils or dust, can weaken adhesion.
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature: Affects adhesive flow and curing.
- Humidity: Can influence bond strength by interacting with adhesive chemistry.
Adhesive Properties
The formulation, viscosity, and curing mechanism of the adhesive determine its performance.
Applications of Adhesive Adhesion
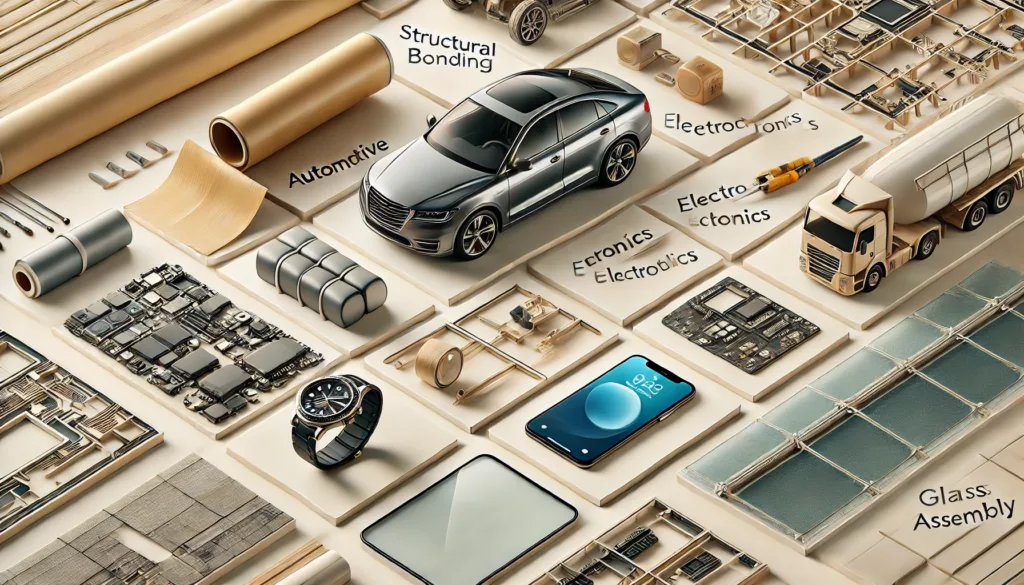

The versatility of adhesive adhesion makes it indispensable in diverse industries:
Automotive and Aerospace
- Adhesives replace mechanical fasteners, reducing weight and improving aerodynamics.
- High-performance adhesives are used in structural bonding and vibration damping.
Construction and Infrastructure
- Adhesives are critical for flooring, paneling, and glass installations.
- Weather-resistant formulations ensure long-lasting bonds.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
- Adhesives bond delicate components in smartphones and laptops.
- Pressure-sensitive adhesives enable easy application in labels and packaging.
Innovations in Adhesive Adhesion
Nanotechnology in Adhesives
Incorporating nanoparticles enhances adhesive properties, improving strength, flexibility, and durability.
Bio-Inspired Adhesives
Inspired by natural phenomena like gecko feet, these adhesives offer remarkable bonding capabilities and reusability.
Sustainability Focus
The development of eco-friendly adhesives minimizes environmental impact while maintaining performance.
Advantages of Adhesion in Adhesives
Seamless Bonding
Adhesives enable clean, seamless bonds without the need for visible fasteners.
Stress Distribution
Adhesives distribute stress uniformly across bonded surfaces, reducing the risk of failure.
Material Compatibility
Modern adhesives bond a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Challenges and Limitations
Environmental Degradation
Extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and moisture can weaken adhesive bonds over time.
Application Sensitivity
Improper application or curing can compromise adhesive performance.
Future of Adhesive Adhesion
The future of adhesives is bright, with advancements poised to expand their applications:
- Smart Adhesives: Responsive to external stimuli like heat or light.
- Recyclable Adhesives: Promote sustainable manufacturing.
- Multi-Functional Adhesives: Combine bonding with properties like conductivity or insulation.
FAQs
What is the difference between adhesion and cohesion?
Adhesion refers to bonding between different materials, while cohesion is the attraction between molecules within the adhesive itself.
Why is surface preparation important for adhesion?
Surface preparation removes contaminants and ensures optimal interaction between the adhesive and substrate, enhancing bond strength.
Can adhesives bond dissimilar materials?
Yes, modern adhesives are designed to bond materials like metal to plastic or composites effectively.
How do environmental conditions affect adhesion?
Extreme temperatures, humidity, or UV exposure can alter adhesive properties and weaken bonds over time.
What are bio-inspired adhesives?
These are adhesives modeled after natural systems, such as gecko feet, offering unique properties like reusability and strong bonding.
Are adhesives environmentally friendly?
Many adhesives are becoming eco-friendly, using bio-based materials and reducing harmful chemicals in their formulations.
Conclusion
The adhesion of adhesive is a fascinating interplay of science and engineering, enabling transformative innovations across industries. Whether bonding metal to metal, plastic to glass, or any combination of materials, adhesive technology continues to push boundaries. By understanding the principles of adhesion and leveraging cutting-edge advancements, industries can achieve stronger, more efficient, and sustainable solutions for bonding challenges.