Electronics assembly adhesives play a vital role in the manufacturing and performance of modern electronic devices. These specialized adhesives are used to bond, insulate, and protect components in products ranging from smartphones and wearables to industrial equipment. This guide delves into the types, applications, and benefits of electronics assembly adhesives, helping you make informed decisions for your projects.
What Are Electronics Assembly Adhesives?
Electronics assembly adhesives are bonding agents specifically designed for assembling and protecting electronic components. They offer excellent adhesion, electrical insulation, thermal management, and environmental resistance, making them indispensable in the electronics industry.
Types of Electronics Assembly Adhesives

-
Epoxy Adhesives
- Known for their exceptional strength and durability.
- Ideal for structural bonding and potting applications.
-
Silicone Adhesives
- Flexible and resistant to heat and moisture.
- Commonly used for sealing and insulating components.
-
Acrylic Adhesives
- Fast-curing with strong adhesion to a variety of substrates.
- Suitable for high-speed assembly lines.
-
UV-Curable Adhesives
- Cures quickly when exposed to UV light.
- Perfect for precision assembly and optical applications.
-
Conductive Adhesives
- Provides electrical or thermal conductivity.
- Used in circuits, sensors, and thermal management.
Applications of Electronics Assembly Adhesives
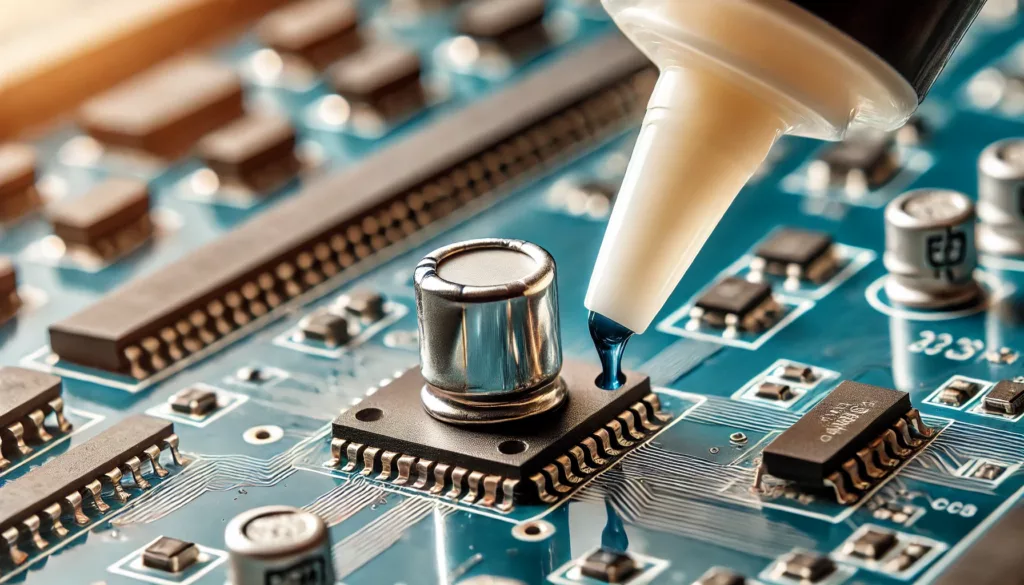
1. PCB Assembly
Adhesives secure components on printed circuit boards, ensuring stability under stress and vibrations.
2. Encapsulation and Potting
Used to protect delicate components from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage.
3. Thermal Management
Thermally conductive adhesives are used to bond heat sinks and dissipate heat in high-performance electronics.
4. Sealing and Insulating
Silicone adhesives seal and insulate enclosures, preventing environmental damage to components.
5. Flexible and Wearable Electronics
Adhesives bond components in devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers, ensuring flexibility and durability.
Benefits of Electronics Assembly Adhesives
- Enhanced Reliability: Protects components from mechanical and environmental stress.
- Improved Durability: Extends the lifespan of electronic devices.
- Design Flexibility: Enables compact and complex designs in modern electronics.
- Thermal and Electrical Management: Supports efficient heat dissipation and electrical conductivity.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Some adhesives are formulated with low VOCs, aligning with sustainability goals.
How to Use Electronics Assembly Adhesives Effectively
1. Prepare the Surface
- Clean and dry surfaces to ensure proper adhesion.
- Remove dust, grease, or residues with alcohol wipes.
2. Apply the Adhesive
- Use a syringe, nozzle, or applicator for precise placement.
- Dispense a thin, even layer to avoid overflow.
3. Cure the Adhesive
- Follow the manufacturer’s curing instructions.
- UV-curable adhesives require exposure to specific wavelengths for curing.
4. Test the Assembly
- Inspect the bond strength and alignment before proceeding with further assembly.
Trends in Electronics Assembly Adhesives
- Miniaturization
Adhesives are evolving to support smaller and more intricate components in compact devices. - 5G and IoT Expansion
High-performance adhesives are essential for the reliable assembly of devices in 5G networks and IoT ecosystems. - Sustainability
The development of eco-friendly adhesives with reduced VOC emissions is gaining traction. - Advanced Thermal Management
Demand for thermally conductive adhesives is growing due to high-power devices like EV batteries and data centers.
Challenges in Using Electronics Assembly Adhesives
- Precision Application: Requires accurate dispensing to avoid defects.
- Compatibility: Not all adhesives work with every substrate or application.
- Cost: High-performance adhesives can be expensive.
- Cure Time: Some adhesives require longer curing times, impacting production speed.
FAQs
What are electronics assembly adhesives used for?
They bond, seal, and protect components in electronic devices, ensuring durability and performance.
Which adhesive is best for PCB assembly?
Epoxy and UV-curable adhesives are commonly used for PCB assembly due to their strength and precision.
Are electronics assembly adhesives heat-resistant?
Yes, many adhesives, like silicone and thermally conductive adhesives, are designed to withstand high temperatures.
How do adhesives improve thermal management?
Thermally conductive adhesives dissipate heat by bonding heat sinks or spreading heat evenly across components.
Can adhesives replace mechanical fasteners in electronics?
Yes, adhesives often replace screws and clips, especially in compact and lightweight designs.
What safety measures should be taken when using adhesives?
Work in a ventilated area, wear protective gear, and follow manufacturer instructions to avoid exposure to harmful fumes.
Conclusion
Electronics assembly adhesives are an integral part of modern electronics manufacturing, offering solutions for bonding, insulating, and protecting components. As technology advances, the role of adhesives becomes even more crucial in supporting miniaturization, performance, and reliability. Whether for PCB assembly, thermal management, or flexible devices, selecting the right adhesive can significantly impact the efficiency and durability of your projects.











